|
|
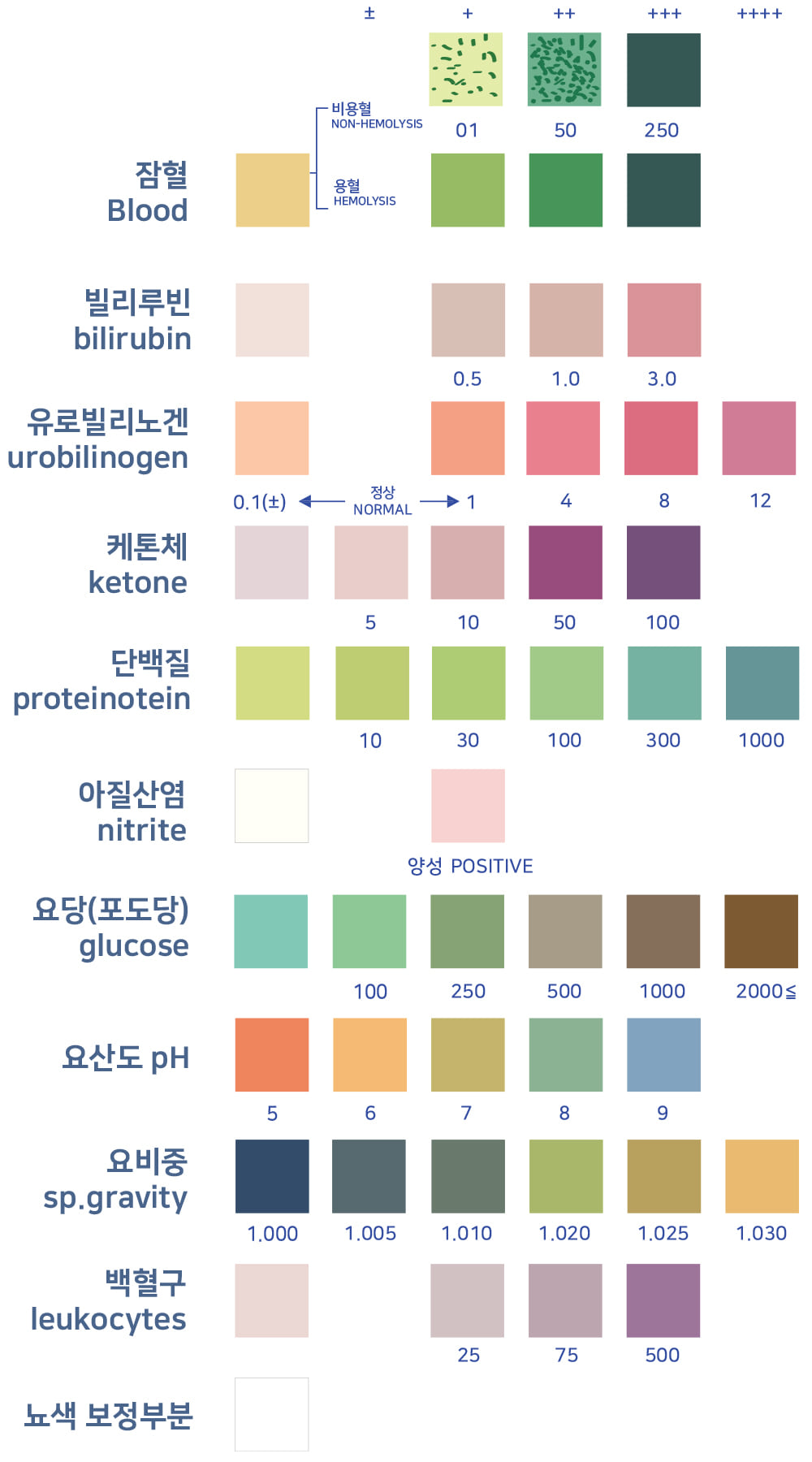
Health check with a total of 10items
Urinalysis is an easy and simple test that
checks various diseases by analyzing the urine, which is excreted from our body by filtering waste products through the organs.
Urine is not just a stinking waste product, but is a 'test paper' that determines the condition of our body.
Urine is produced by filtering blood that circu- lates throughout the body. That is, the blood is raw material of urine. The blood is filtered at a region in the kidney called 'glomerulus'.
When blood from the kidneys passes through the glomerulus, a portion of larger blood com- ponents such as blood cells and large proteins are exchanged and are excreted. This compo- nent can be detected with a test strip.
Urobilinogen is a byproduct of bilirubin, a component of bile produced from the liver; urobilinogen is excreted through urine. By detecting urobilinogen, a liver and kidney abnormalities, such as chronic hepa- titis and jaundice, can be speculated.
Using a strip that can react to the metabolites contained in the urine, you can check the basic health status of the body by soaking the strip with urine and monitoring the response to 10 items.
|
|
|
occult blood
a mixture of blood in urine
Suspected urological damage or tumor
Hemorrhagic cystitis, urinary stones, nephritis, tumors of the kidney and bladder
A occult blood test is to test for the presence of red blood cells or hemoglobin (Hb) in the urine. In the test strip method,
it detects benzidine which is oxidized by the peroxidase of red blood cells. The sensitivity is high enough to detect single blood cell and show positive results.
There may be red blood cells in the urine even if there is no visible hematuria.
Urinary system tumors, damage to the urinary system (ureters, urinary tract, etc.), and hemolysis are the causes of occult blood positive results.
Women who are menstruating may also have a positive occult blood results.
Hematuria means bleeding from the urinary tract and urinary system.
Hemoglobin can be false-negative in the presence of strong reducing substances, so if vitamin C is detected in the urine test,
microscopic examination is performed even if the test strip is negative to avoid missing occult blood.
A glomerular disease may be suspected if hemoglobin, proteinuria, or altered red blood cells are seen.
|
Bilirubin
Suspected liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, gallstone biliary tract disease
It can be an early indicator of jaundice.
Jaundice also occurs in pets such as dogs and cats.
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment found in bile, a liquid produced by the liver. If even minute amounts of biliru- bin are found, it is considered abnormal. The color that urine bilirubin may appear on the test strip is light brown to dark brown.
Even in normal condition, when bilirubin is bound to bilirubin glucuronidie in the liver, it becomes water-soluble and can be excreted in the urine, but the amount is not so large that it can be detected as an immersion band.
Elevated bilirubin levels may indicate several liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and gallstone biliary tract disease, and may also be an early indicator of the development of jaundice. These symptoms (jaun- dice) also appear in pets such as dogs and cats. However, the reaction is more intense, compared to a strong human body.
|
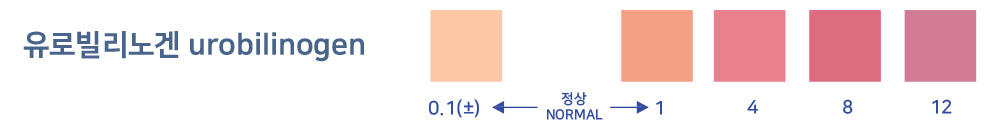
Urobilinogen
Liver disease (hepatitis, mitigation, liver damage), suspected anemia
Urobilinogen is produced by reduction of conjugated bilirubin in bile by enterobacteria in the lower small or large intestine. Most are excreted in the feces,
but about 20% is excreted from the intestines back into the bile through the liver,
some of which passes through the liver into the systemic circulation and is excreted by the kidneys.
A positive urobilinogen result may be caused by liver disease (I.g, viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver damage), a drug/toxic substance, or hemolytic anemia.
If urobilinogen levels are low or absent, such as due to liver dysfunction or long-term use of antibiotics, it may indicate the possibility of liver or biliary obstruction.
In hemolytic jaundice and neonatal jaundice, urine bilirubin is negative but urine urobilinogen is positive. Both urine bilirubin and urobilinogen are positive in hepatocellular
jaundice, such as liver cancer, cirrhosis, and hepatitis, and negative in common bile duct obstruction.
|
Ketone bodie
Even when diabetic ketoacidemia is present in severe diabetes, the urea body
increases significantly.
Even non-diabetics may be temporarily positive due to stress during surgery.
Ketone bodies are produced by the liver as metabolites of fat. When the intake of carbohydrates is insuffi- cient, such as starvation or fasting,
or when it is difficult to use glucose as energy, such as diabetes, fat is converted into fatty acids instead of glucose and used as energy.
At this time, fatty acids are converted into ketones in the liver and excreted in the urine,
causing ketonuria. Also, when these ketones are not excreted in the urine or broken down, ketosis can occur.
Examples of ketone-positive include diabetes, hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, Cushing's syndrome, pheochro- mocytoma,
long-term fasting or starvation, stress, infection, fever, exercise, trauma, severe vomiting, diarrhea, and drug addiction; false-positive urine ketone bodies may occur in phenylketonuria.
In particular, ketones increase significantly in diabetic ketoacidosis led from severe diabetes.
Pheochromocytoma is a catechol- amine-producing tumor that occurs in the adrenal medulla and causes headache, sweating, and palpitations during attacks.
It shows higher results in severe diabetic patients; diabetic ketoacidosis should be suspected if it is more than 3 mm.
Even non-diabetics may temporarily become positive due to stress after surgery. In case of insufficient glucose (fasting, starvation, vomiting, diarrhea, etc.),
the ketone bodies may be positive, and a positive result can also be confirmed in the case of excess fat due to obesity or drinking.

|
protein
chronic diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure, Bubble urination and fatigue
It indicates the level of protein in the urine. When the kidneys are functioning normally, they reabsorb the protein filtered by the glomerulus and return it to the blood.
Turbid, cloudy, or foamy urine is a symptom of proteinuria, but there are cases where proteinuria is not detected during actual examination.
Therefore, it is important not to worry in advance and to confirm accurately with a urine test at the hospital.
For chronic diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure, measuring proteinuria on a regular basis is helpful in disease management.
|
Nitrate
Bacterial infection, urinary tract infection (bladder inflammation, nephritis, etc.) can be suspected.
If the test strip test is positive, the positive predictive value of urinary tract infection (UTI) reaches 96%, so antibiotics can be prescribed without culture test results.
However, UTI cannot be ruled out even for negative results.
Infections with non-nitrite-producing bacteria, such as gram-positive cocci or fungi, such as group B streptococci, show false-negative.
Because it takes 4-6 hours for bacteria to reduce nitrate to nitrite, urine retention in the bladder shorter than this may result in negative results.
Therefore, the first urine in the morning, which has been collected in the bladder overnight, is suitable as a sample.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is known to accompany great pain, such as fever, lower abdominal pain, and dis- comfort when urinating.
Also, urine can have a strong ammonia odor, even if it is not properly excreted. Urinary tract infections may also appear on a negative nitrite test.

|
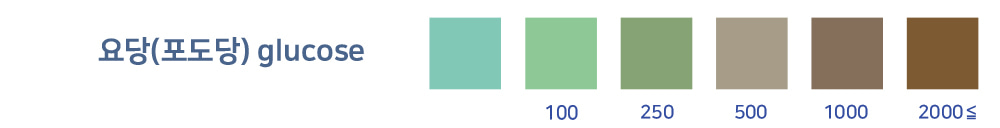
urine glucose
Diabetes, Cushing's syndrome, and kidney inflammation can be suspected.
It refers to the presence of glucose in the urine. Our blood contains a certain amount of glucose, which is called blood glucose,
Blood glucose is catabolized into energy by insulin secreted from the pancreas, and the rest is excreted from our body. In a healthy individual, glucose is reabsorbed by the tubules and goes back to the blood,
but individuals with kidney problems or hyperglycemia, the glucose will be excreted through the urine.
When the level of urine glucose excreted through the urine exceeds 1g and appears to be above the normal value, but at the same time, the blood glucose level is within the normal range,
which is called renal glycosuria. It is found very often even when there are no symptoms, and since there is no clear medical evidence that it causes diabetes,
it is recommended to check the test results at regular check-ups once a year.
|
ph
Investigate the acidity and alkalinity of urine.
+ Alkaline urination: acute/chronic renal disease, metabolic and respiratory alkalemia - vomiting, urinary tract infection
+ Aciduria: Metabolic and respiratory acidemia, severe diarrhea, sobbing, dehydration
The reagents used in the test strip method, methyl red and bromothymol blue, change color depending on the pH of the urine; methyl red pH 5.0(red)~ pH 6.5(yellow), bromothymol blue pH 6.0(yellow) ~ pH 8.0 (blue).
In general, normal urine is slightly acidic and most of it corresponds to pH 6~ 6.5.
The pH fluctuates between 4.5 and 8.0 depending on the dietary content. People tend to have aciduria after animal-based meals, fever, diarrhea, dehydration, and strenuous exercise,
and alkalineuria after plant-based meals. During sleep, acid urine is caused by respiratory acidemia, in the morning alkaline urine is caused by excretion of bicarbonate accumulated at night,
Immediately after a meal, stomach acid is secreted and cause alkalemia, resulting in alkaline urine.
If the pH value is high or low, it may cause kidney damage,
gastric lavage, urinary tract infection (UTI), vomiting, dehydration, diarrhea, and diabetic ketosis to occur. It also creates an environment where kidney stones can form. Moreover,
depending on the urine protein concentra- tion in the urine test, the test strip changes from yellow (negative) to yellow-green, green, and pure blue. As such,
pH is an important indicator of kidney, gastrointestinal, respiratory and metabolic health.

|
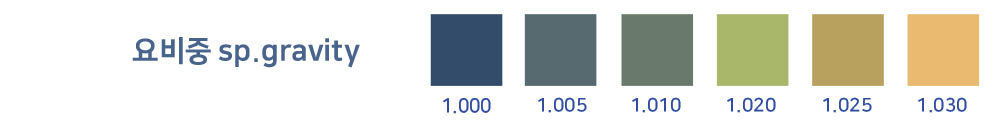
Specific gravity of urine
+ High Specific gravity of urine : severe dehydration, diabetes, proteinuria
+ Low Specific gravity of urine : damage to the renal tubule
Specific gravity (weight per unit volume) refers to the amount of solute. Specific gravity of urine is a measure of urine concentration,
comparing the amount of dissolved substances in urine by comparing urine specific gravity measurements to pure water.
The range of specific gravity of urine for healthy adults is between 1.003 and 1.030.
Both high and low specific gravity of urine is normal. Low specific gravity values indicate impaired ability to concentrate urine due to medical conditions such as insipidus, sickle cell nephropathy,
or acute tubular necrosis. Conversely, a high value indicates high urine glucose, concentration due to dehydration, or high protein or ketonic acid concentration.
If the specific gravity is low even though the patient is dehydrated, renal failure may be suspected as the reabsorption function is decreased.
|
Leukocyte
urethral inflammation, bladder inflammation, nephritis
Pyuria is urine with pus, which is caused by leukocyte. Pyuria is defined as the presence of three or more leukocytes
(at high microscopic magnification) in the centrifuged sediment of urine. In the test strip method, pyuria is diagnosed by detecting leukocytes esterase produced by neutrophils.
Pyuria suggests possible inflammation and infection of the kidney-urinary tract, such as urethritis, cystitis, and nephritis.
The results of nitrites and leukocytes esterase alone can diagnose urinary tract infections with high sensitivity and specificity.
The response may decrease and false negatives may be obtained if the urine specific gravity is high, urine glucose is high, or if oxalic acid or cephalosporin (cephalosporin) antibiotics are administered.
If there is a lot of vaginal discharge, the leukocytes in the urine may come out as false-positive.
|